
Diabetes is a severe condition, and proper care is crucial to staying healthy. Therefore, the best way is to consider managing diabetes with diet and exercise. This way, you prevent the condition from becoming more critical. Remember that diabetes can be life-threatening, and some ailments associated with diabetes can lead to stroke, heart attack, and heart diseases. Fortunately, there are various diabetes management tips that you can follow.
What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a longterm condition that occurs when the pancreas is unable to regulate the body’s sugar levels. It has no cure, but it is manageable. Additionally, there are three types of diabetes: that’s type one, type 2, and gestational diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition that makes the immune system unknowingly attack and damage the cells that produce insulin in the pancreas.
Type two diabetes results in insulin resistance, making the body incapable of controlling insulin properly. On the other hand, gestational diabetes occurs in pregnant women, and this results due to the production of insulin-blocking hormones generated during pregnancy.
What are the causes and symptoms of diabetes?
One of the significant causes of diabetes is obesity. In the year 2015 to 2016, the prevalence of obesity in the US was 39.8%, and this is a cause for concern. Remember, there are various conditions associated with obesity, such as type 2 diabetes, stroke, heart diseases, and some types of cancers. Inheritance is also another notable cause of diabetes, which is associated with one’s bloodline.
And this means that if your parents have diabetes, you’re also at a higher risk. Some of the common symptoms of diabetes are; uncontrolled thirst, frequent urination, loss of weight even without exercising, fatigue, stress, and feeling that your hands and feet are wet.
Food guide for diabetics
If you have diabetes, you must follow a strict diet. This way, you can easily keep your condition in check and stay healthy. Most doctors also advise that people with diabetes should try to lose weight to a certain extent. And this helps in lowering blood pressure, blood sugar, and cholesterol levels. This way, you feel more energetic and healthier.
Below are the steps to the best diabetic diet:
1. Opt for high fiber foods
Carbohydrates can affect your sugar levels, and you should make healthy adjustments if you’re to have a proper diet. Examples of foods that you should consume in limited portions are pasta, potatoes, starchy grains, sodas, candies as well as bread. These types of foods and any other carb-rich food sources elevate blood sugar levels.
Therefore, opt for high fiber carbohydrates, also known as slow-release carbs. These are digested gradually as compared to other food items. Some examples of high fiber foods are brown rice, yams, sweet potatoes, whole-wheat pasta, peas, low sugar bran flakes, and green leafy vegetables. Moreover, incorporate a lean protein and minimal fats in every meal or snack.
2. Consistent meals
Having regular meal times is very important for people with diabetes. When you don’t eat, your blood sugar may become too low. But it becomes too high when you eat often. In every two to three hours, eat a meal or snack, going for long hours without taking anything is not right for people with diabetes. You can as well consult with your doctor or diabetic educator on the best choice for you regarding meal timing.
Moreover, when preparing your meals, check what’s written on the food label. Also, be sure of the food sizes, ingredients, or any additives contained in the product. Some include elements that may add to your sugar intake, and it’s crucial to beware of everything that you consume. For overweight diabetics, it’s advisable to consult your doctor concerning natural supplements that you may need to take to shed excess weight or control your blood sugar.
3. Plan your portion sizes
Excess calories result in excess weight and excess body fat. Having type 2 diabetes and excess weight can be critical. When you’re overweight or obese, this means that you have less sensitivity to insulin, and this is why weight loss and potion control is crucial for all people with diabetes.
Therefore, for your meals and snacks, carefully plan out your portion sizes and remember the too much or too little can either elevate or lower your glucose levels. If not sure how to measure your portions, your dietician can guide you on how to do this.
4. Food flavoring
Instead of adding sugars to foods for flavor, use other spices and seasonings like lemon juice, herbs, spices, garlic, mustard, and garlic extracts, for example, peppers, almond, or salsa. If your recipe requires some oil, opt for canola or olive oil.
More so, ensure that you brush your teeth after eating food flavored with your favorite spices. To completely get rid of any smell from the food flavor, use the best vegan toothpaste and be sure of a fresh breath no matter the type of spices used.
5. Choose your fats wisely
There are different types of fats; some are unhealthy, while others have numerous health benefits. And this makes it vital to pick your fats carefully.
Unhealthy fats
The most unhealthy fats are artificial transfats. They are ordinarily used to prevent vegetable oil from getting spoiled. Are you wondering what foods to avoid with diabetes? Shun commercially baked products, packaged snacks, fried foods, or any food containing partially hydrogenated oil in the ingredients- even if it’s marked to be trans fat-free.
Healthy fats
Unsaturated fats are the most robust. They usually come from fish and plant sources, for example, olive oil, nuts, and avocados. Omega 3 fatty acids are beneficial in the body; they combat inflammation and also promote brain and heart health. Some of the great sources of omega 3 are salmon, tuna, and flaxseeds.
Saturated fats
these are primarily found in topical oils, red meat, or dairy. You don’t need to exclude saturated fats from your diet, but use them in moderation.
6. Make a glycemic index (GI)
The glycemic index guides you on how long your body takes to turn a particular food item into sugar. High GI foods can elevate your blood sugar and should be taken in low quantities or only opt for low GI foods. Another method of classifying your foods is by categorizing them as fire foods with a high GI, water foods that you can consume in any amount, and coal foods with a low GI.
Fire foods
These are foods that contain low quantities of protein and fiber. Examples of fire foods include things such as white rice, potatoes, white bread, pasta, and baked foods. You should also limit or avoid processed foods and snacks; they are unhealthy and can worsen your condition.
Water foods
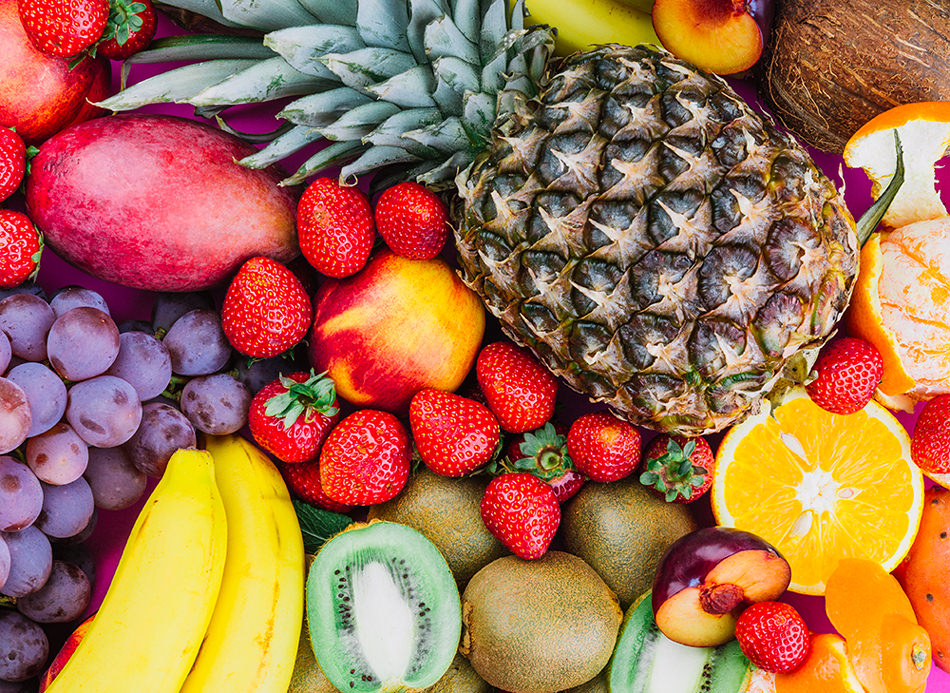

These are also referred to as free foods and don’t alter your blood sugar levels. Water foods are suitable for the diabetes diet, and you can eat them as much as you want. They include most vegetables and fruits. The best fruits for people with diabetes are grapes, apples, berries, citrus fruits, mangoes, and pineapples. Opt for fresh fruits and cut of fruit juices with added sugar and dried fruits.
Coal foods
These are excellent choices to fire foods, and you must always incorporate them into your diet. Coal foods are high in fiber and protein. Examples of great coal foods are nuts, seafood, whole grains, seeds, lean meats, and brown rice.
What about the exercises?
There are different diabetes management tips, but you can’t overlook exercises. Exercising is a significant pillar in the management of diabetes. Besides, obesity can aggravate your condition, and you can avoid this by excising regularly and following a proper diet.
Examples of exercises ideal for type 2 diabetics:
1. Aerobics
Aerobics training is essential for diabetics, and this involves all activities that can raise your heart rate, for this aids in lowering sugar levels and body mass. Aerobics lessen the risk of heart diseases common to people with diabetes.
They also check diabetes by reducing the risk of obesity, which could result in diabetes. Some aerobics to try out are pursuits like swimming, running, walking, dancing, and many more. Experts advise that people with diabetics should exercise thirty minutes each day or approximately four times weekly.
2. Resistance training
Resistance training is also known as strength training and is another fantastic exercise for people with diabetes, which endeavors to strengthen body muscles. It involves other objects like dumbbells, bricks to tone muscles, and weights. The effects of resistance training are the same as those of aerobics.
The two types of exercises can affect blood sugar control, and combining both of them produces excellent results. However, you should not overdo any kind of workout, for this could result in hypoglycemia, which is caused by low glucose levels.
Besides, when you exercise a lot, your glucose levels can reach unsafe levels, and this may result in fainting and exhaustion. Always monitor your blood sugar levels after workouts; if it’s too low, consider some bites to spike up the sugar.
Conclusion
A great way for diabetes management is to watch what you eat. A healthy, nutritious diet and some exercises are all you need for optimal health in diabetes. Therefore, consider the above diabetes management tips and watch your health change for the better.
References
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (2016). Diabetes Diet, Eating, & Physical Activity. [online] Available at: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/diet-eating-physical-activity [Accessed 11 Jan. 2020].
Harvard Health Publishing. (2020). The importance of exercise when you have diabetes. [online] Available at: https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/the-importance-of-exercise-when-you-have-diabetes [Accessed 11 Jan. 2020].
Harvard Chan. (2020). Simple Steps to Preventing Diabetes. [online] Available at: https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/disease-prevention/diabetes-prevention/preventing-diabetes-full-story/ [Accessed 11 Jan. 2020].
Gray, A. and Threlkeld, R. (2020). Nutritional Recommendations for Individuals with Diabetes. [online] Ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279012/ [Accessed 11 Jan. 2020].




